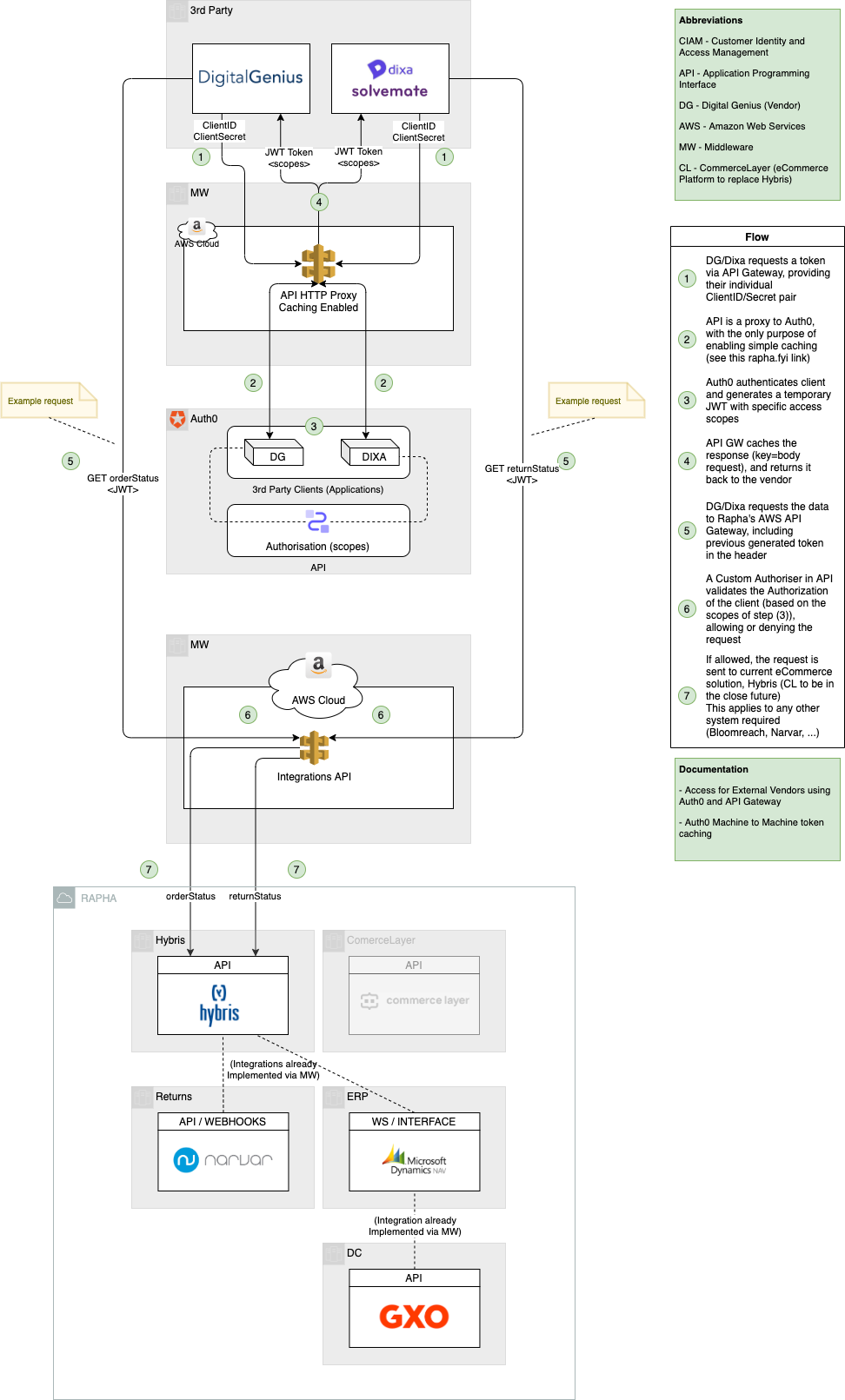
3rd party access to Rapha's systems
Overview
As we continue expanding our composable architecture, we don't centralise data & services in a very reduced number of systems anymore (Hybris, NAV).
Our current Technology ecosystem uses many different vendors / infrastructures to store data and provide services to access or modify that data based on the requirements.
It might happen that an external vendor requires integrating with our composable architecture to pull/push information, or to perform actions that are captured in a business logic case.
Also, as defined in our Architecture Manifesto, we decided not to allow ad-hoc integrations anymore, but use a Middleware that provides such integration.
With all the previous facts, one of the key players on following our pincipiples and architecture consistentcy is the Authentication & Authorisation implementation.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of checking the credentials provided by a vendor.
If those are valid, a scope (or multiple scopes) are assigned to that vendor, which will define, later on the Authorization process, if the vendor can execute a particular action (pull/push data, perform an action, etc...)
Authorisation
Authorisation is the process of deciding if a vendor can perform an action.
This decision is made based on the scope/s assigned on the Authentication process to a vendor.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) - Auth0
We currently use Auth0 as the platform of choice to support our access & security requirements.
General Architecture & Procedure
The solution considers three blocks:
- AWS API for caching M2M Auth0 tokens, as a quick solution for the quota issue (see spike documentation)
- Auth0 with the 3rd party client credentials (id & secret), and the definition of the scopes
- AWS API for access control to Rapha inner systems (currently but not restricted to, this could include any system we have access to)
In terms of procedure, the following sequence applies:
- 3rd Party client exchanges with Auth0 their credentials for a JWT containing the access details
- This exchange happens via an API gateway, with the purpose of caching the JWT tokens generated by Auth0 per client (see the quota issue link above)
- Finally, the client sends a request (including the previous step's JWT) to the integration API endpoint required which validates the authentication & authorisation details, and if allowed, orchestrates the access to the Rapha systems.
Please notice that this integration API can work in any desired form, from a simple bypass one of the Rapha systems, to a more complex MW service (e.g. Lambda, Eventbridge, ...) which contains a specific business logic.